Digitalization and 4.0 Industry
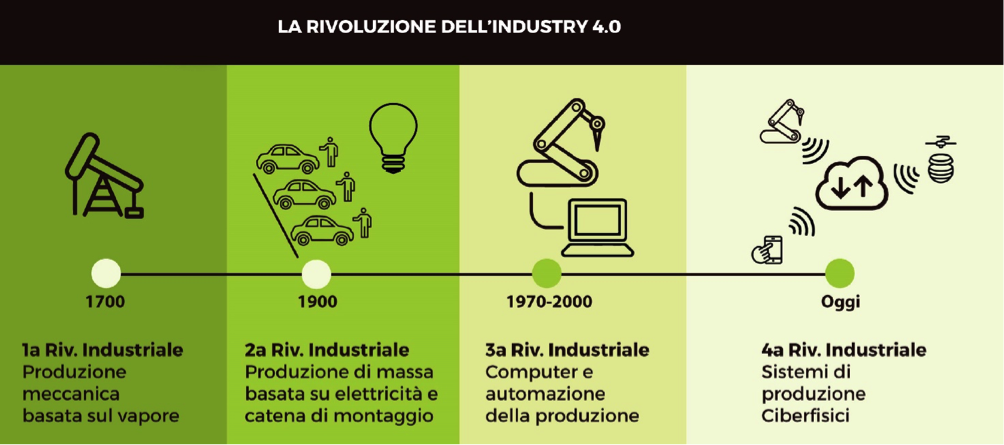
The first industrial revolution used the power of steam to mechanize manual work. The second used electricity to develop mass production. The third used electronics and information technology to automate production. The fourth revolution, or Industry 4.0, envisages the digital transformation of the industrial system, thanks to a combination of technologies that allow to create an ecosystem of factories, machines and intelligent objects able not only to communicate with each other, but also with the surrounding environment.
One way to describe the elements of digitalisation is described in the circular 4/E of the Ministry of Economic Development and the Revenue Agency of 2017. According to the authors of the circular, the digitalisation process is divided into 5 directions:
- Interconnection – The possibility that a good exchanges information with internal systems, for example with the management system
- Virtualisation – The ability to create a “virtual copy” of the real system
- Decentralization – The possibility that the several components that make up a production plant implement appropriate strategies (e.g. to correct process drifts)
- Remote Interaction – The ability to access various devices remotely to collect data on operation (e.g. remote maintenance)
- Real-time processing and reaction – The ability to collect process data in real time and perform related actions
Technological elements of the Industry 4.0
Advanced production systems can be represented by autonomous robots and intelligent machines. Autonomous robots are anthropomorphic and mobile robots that are able to cooperate with each other and with humans and that can be programmed easily.
Intelligent machines are machines with a great capacity to adapt to the variability of the production environment. In these machines, the interaction with man is pushed to the maximum and is expressed in two ways: through the feed-back of data that can be profitably used for the application of data analytics and through the man-machine interface.
The term additive manufacturing means the manufacturing process by adding layer-upon-layer of liquid, solid or powder material. Additive manufacturing is no longer considered as a mere technology for rapid prototyping, but as a real production technology for the manufacturing of components and finished products.

Augmented Reality technology allows the enrichment of reality by adding virtual information that is detectable by the user in real time.
The integration promoted within the Industry 4.0 is characterized by the external dimension (i.e. the integration between suppliers and customers of the same supply chain) and the internal dimension (i.e. the mutual communication between the machines of the factory).
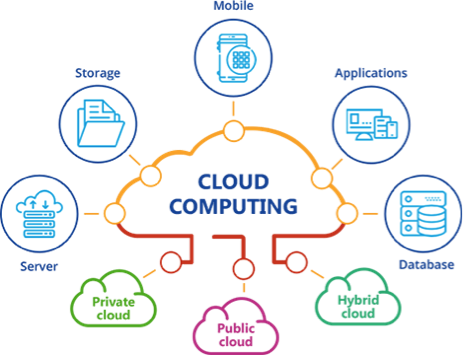
Cloud computing is defined as a model that allows widespread, dedicated, on-demand network access to a group of configurable resources.

Big Data-The extended volume, variety and speed of data from the machines in the factory must be managed with appropriate tools and it is very important for 4.0 Industry
Evolution of volume and variety
The elements that characterize this economic and social period are speed and flexibility that result in a strong complexity when managing the production and distribution processes. Despite the stimuli that originate from the concepts of intelligent manufacturing, it remains difficult to overcome the Taylorism model of production on which companies have been established and have evolved. Idral, on the other hand, tries to implement the organizational model of a manufacturing company in the age of technological innovation, i.e. more and more oriented towards management by flows and no longer by homogeneous processes. The challenges to be faced can be characterized by:
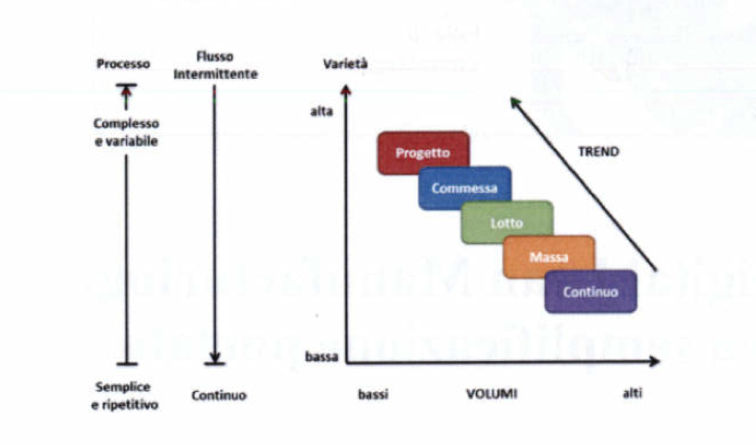
- Increasingly lower volumes
- high variety (customization) and complexity of the product
- intermittent flows
- complex and variable processes
The faster design and industrialisation, and the lower costs of prototyping activities, allow for greater customization of products.
Lean production process
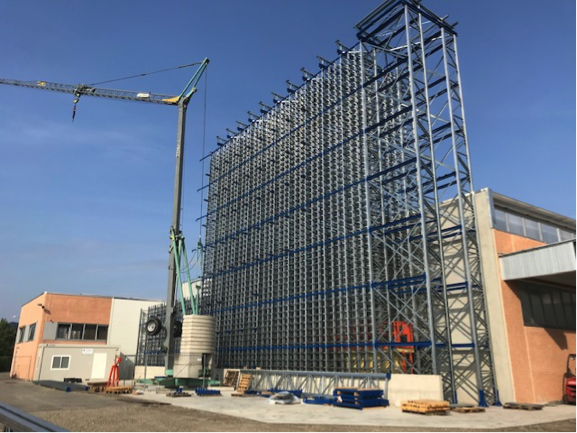

The construction of an automatic warehouse in Idral for the supply of components to the assembly table in real time linked to the production order of the product to be assembled represents a change in the innovative production process and helps, thanks to the support of technologies, to reduce production times and makes the production process more lean.
The scope of digital transformation is greater than in the past. It is not easy to combine different technologies to create product or process innovation. It is clear that we need to invest in technology, but it must be accompanied by a reorganisation of processes to accommodate these technologies as well as by training for the people who will then have to use and exploit them. The current trend towards the retraining of labour will be clearly consolidated in the future. Not the fear of possible job losses, but the courage and confidence in one’s own abilities, the willingness to qualify and the choice to implement digitalisation mark a significant improvement in competitiveness and, with it, also the success of our company. Our committed, skilled and productive employees are and remain the main and irreplaceable success factor.
One of the main objectives of digitalisation within the factory, especially in the production-logistics area, is undoubtedly to increase the efficiency of processes.
Product innovation and customer relations
In addition to this aspect, there are also impacts on the products and services offered and the way of interacting with customers. Product positioning and service rational are influenced by the introduction of digital technologies in the industrial area.

By Ing.J.Schweitzer
Head of Manufacturing and R&D










